1.Primary key is a subset of Candidate key
2.Candidate key is a subset of Super key
3.Every Candidate key is a super key but every Super key is not a candidate key
1. SUPER KEY:
A Super key is a combination of all possible attributes that can uniquely identify the rows or tuples in the given relation
A Super key is a combination of all possible attributes that can uniquely identify the rows or tuples in the given relation
- Super key is a superset of a candidate key.
- A table can have as many as super keys.
Note:
If the given table is with n attributes (eg: for 5 attributes ) then the maximum super key present in the given table is
2^n - 1
2^5 - 1= 31
Example:
2.CANDIDATE KEY:
It is
defined as a minimal super key (or)
irreducible super key.(or) An
attribute (or) A combination
of attribute that identifies the record uniquely but none of its proper subset can identify
the record uniquely.
Example: sid
sname, saddress
Here sid key
can identified the record uniquely.
Similarly
combination of sname and saddress can
identified the record uniquely but
neither sname (nor) saddress used to identify the record uniquely.
Note:
1.Super key whose proper subset is not a super key
2.Minimal super key
Example:
s1={1,2,3} and s2 = {1,2}
subset (⊆) : All the members of s2 must be in s1
s2 ⊆ s1
Proper subset (⊂ ) :All the members of s2 must be in s1 and All the members of s1 must not be in s2
s2 ⊆ s1 and s1 ⊈ s2
Example:
s1={1,2,3} and s2 = {1,2,3}
subset (⊆) : All the members of s2 must be in s1
s2 ⊆ s1
Proper subset (⊂ ) :All the members of s2 must be in s1 and All the members of s1 must not be in s2
s2 ⊆ s1 (T) and s1 ⊈ s2 (F) so this is not a proper subset
3.ALTERNATE KEY:
Out of all candidate keys, only one gets selected as primary key, remaining keys are known as Alternate keys
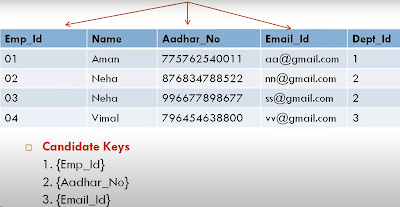
Example:
In the Employee table.
Emp_id is best suited for the primary key
Rest of the attributes like Aadhar_No, Email_id are considered as a Alternate keys.
4.PRIMARY KEY :
A Primary key is one of the candidate key chosen by the database designer to uniquely identify the tuples in the relation
- The value of Primary key can never be NULL.
- The value of Primary key must always be unique(not duplicated)
- The value of Primary key can never be changed i.e no updation is possible.
- A relation is allowed to have only one Primary key.
Example:
5.Foreign (or) referential key (or) integrity :
A foreign key is an attribute (or) combination of attributes in one base table
that refers to others key of another table. The purpose of the foreign keys is
to ensure the referential integrity of the data
that which appear in the database are permitted.
Note: Let R1(a,b,c) and R2(x,y,z) be two relations in which 'a' is foreign key in R1 that refers to primary key of R2.consider four options
a) Insert into R1
b) Insert into R2
c) Delete from R1
d) Delete from R2
which is correct regarding referential integrity?
1) option a and b will cause violation
2) option b and c will cause violation
3) option c and d will cause violation
4) option d and a will cause violation
Ans: R1(a,b,c) [Referencing Table] with 'a' --> "FK" and R2(x,y,z) [Base Referenced Table] with 'x' --> PK
6. Composite key:
If we use multiple attributes to create a primary key then such type of
keys are called composite key.
Eg : std (sid, sname ,sadd)
Sub
(subid,subname,credit,sid)
Marks(sid sname subid subname
marks results)
















No comments:
Post a Comment